Guide to stainless steel immersion passivation for industrial applications
September 20, 2023Passiver stainless steel guarantees the longevity and reliability of stainless steel components
Stainless steel is widely recognized for its resistance to corrosion. This makes it a preferred material in a wide range of industrial applications, such as the food and aerospace industries. However, even stainless steel can suffer from corrosion if not properly maintained. Passivation is therefore a crucial process. It improves the corrosion resistance of stainless steel by promoting the formation of a protective oxide layer on its surface. Discover in this article the key steps and best practices for passivating stainless steel in immersion.
What is passivation?
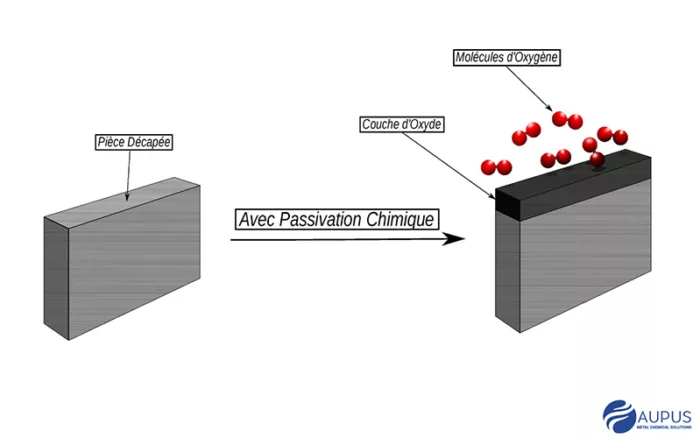
Passivation is a chemical surface treatment process that promotes the formation of a passive, protective oxide layer, also known as chromium oxide. More homogeneous, it is also thicker than natural passivation. This oxide layer acts as a barrier, preventing corrosion and improving the material's durability. Passivation is particularly important for stainless steel components that come into contact with corrosive substances or environments.
The equipment needed to passivate stainless steel
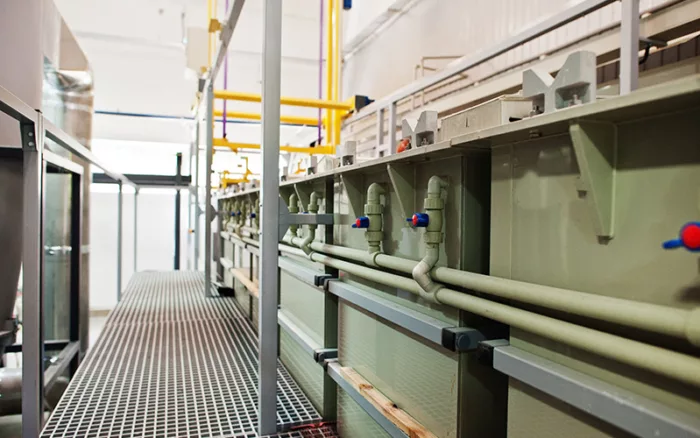

Passivation treatment is primarily carried out in a chemical bath. You'll need a plastic tank, maintained at room temperature, in which to immerse your metal parts. We also recommend adding a rinsing tank, preferably supplied withdemineralized water. The choice of passivation product is also crucial for a good finish. Products differ in the type of acid used in their composition. We offer two types of solution for two different applications. Aupus 967 A is anitric acid -based product for passivating austenitic stainless steel parts. Aupus 967 AM is based oncitric acid and is designed to passivate austenitic and martensitic stainless steel parts. All our products are ready-to-use.
Steps for immersion passivation of stainless steel

1/ Safety precautions before passivating stainless steel
Before starting the passivation process, please ensure that all safety measures are in place. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE ), including gloves and safety glasses. Work in a well-ventilated area. When applying a nitric acid-based passivator, wear acid-resistant gloves. Contact our team for advice on wearing the rightpersonal equipment for your application.
2/ Surface preparation
First, start by cleaning surface of the stainless steel to remove all visible contaminants: dirt, grease and scale. To do this, use an alkaline or acidic degreasing solution. For this step, we recommend our Aupus Decapoli 15. Thisphosphoric acid-based product removes all grease. Rinse the surface with clear water to remove any residues of cleaning agents. For best results, usedemineralized water instead of clear water. Clear water can leave limescale on your stainless steel parts.
In most cases, a pickling treatment is recommended in addition to degreasing. Pickling eliminates iron oxides created by contact with air or during heat treatment and welding operations.
3/ Immersion
To passivate your parts, immerse the stainless steel parts in the passivating solution, making sure they are completely submerged. We recommend ourcitric acid-based, nitrate-free passivator Aupus 967 AM for austenitic and martensitic stainless steels. Immersion time may vary according to stainless steel grade and surface preparation. However, it is generally around 30 min.
Temperature control: Keep the passivation solution at the specified temperature, in the case of Aupus 967 A C passivator between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F). This temperature control helps optimize the passivation process.
Good to know: Our R&D team can suggest laboratory tests on your parts to determine the optimum operating parameters for your application. Contact us to find out more.
Agitation (optional): To improve passivation, add gentle agitation to the solution to ensure bath homogeneity.
4/ Rinsing
After the specified immersion time, rinse the parts thoroughly with clean water or, preferably, demineralized water. This step will remove all traces of passivating solution. It is crucial to prevent chemical residues from affecting stainless steel performance.
5/ Drying
Dry passivated stainless steel components thoroughly. This will prevent water spots and promote the formation of the protective oxide layer. We recommend the use of adrying oven.
6/ Quality control
Visually inspect passivated surfaces to ensure they are clean, smooth and free of contaminants. To ensure that the treatment complies with customer standards, you may ask to carry out salt spray tests . These tests verify that parts are free from corrosion for a period of time defined by the standards.
Conclusion

Passivating stainless steel in immersion is an essential process for improving its corrosion resistance and maintaining its performance in a variety of industrial applications.
By following the steps described above and adhering to industry-specific standards and regulations, you can increase the corrosion resistance of your stainless steel parts and contribute to safer, more efficient operations.
Our teams will support you in your stainless steel passivation projects by designing customized treatment lines (cleaning line, pickling, passivation, electrolytic polishing) combined with a wide range of stainless steel chemicals anddedicated equipment(pumps, immersion heaters, PPE). Contact us today to discuss your needs.
